Route optimization has a substantial role in logistics efficiency and ensuring that deliveries will arrive on time. But AI driven route planning delivers value only if you can recompute good routes as fast as reality changes, i.e., real-time smart route optimization.
As we know, last‑mile is the most expensive part of fulfillment across a supply chain, often representing about 41% of logistics costs. Hence, even modest improvements compound into real money or savings.
Question: What about bringing in significant AI-driven route planning improvements?
Well, AI-based route planning logistics and optimization, in association with powerful GPUs, can fix the routing problem for good. Let’s find out how faster route re‑planning pays back.
What is Logistic Route Optimization?
Let’s understand the basics first.
Route optimization refers to determining the most efficient and cost-effective channel for goods transportation. It utilizes multiple shortest-path algorithms to determine the most efficient pathway between two points.
Vehicle Routing Problems with Pickup and Delivery (VRPPD), Travelling Salesman Problems and High/Sparse-density Routing are among the more well-known algorithms involved in route optimization.
Additionally, route optimization also incorporates myriad factors such as:
- Delivery time
- Product perishability
- Transportation distance
- Traffic congestion
- Fuel consumption
- Necessary stops during the process
- Delivery downtime
- Vehicle capacity and more.
Most importantly, these factors are accounted for in real-time. In short, computations can get extremely complicated.
This is why modern route planning and logistic optimization solutions depend on GPUs for real-time data capture and computation (more on this later).
Challenges of Traditional Routing in Logistics
Fleets face the Vehicle Routing Problem and variants with time windows, pickups and deliveries, capacities, driver hours, skills and cold chain rules.
These problems are NP‑hard, i.e., extremely complicated. So, the search space grows quickly as stops and constraints increase.
Indeed, heuristics perform better than exact solvers. But, they still spend most of their time evaluating fleet unit moves and checking feasibility. Add live inputs like traffic and dwell times and you must solve repeatedly.
In short, the entire process becomes exhaustive and time-intensive. That is where GPU parallelism changes the equation.
Fun Fact: Did you know USA citizens lost an average of 42 hours to congestion in 2023, costing $733 per driver?
How a Modern Route Optimization Pipelinelooks like?
Modern-day route optimization utilizes high‑performing stacks that follow a three-stage loop:
- Predict the world with models for speeds, ETAs, dwell times and demand.
- Build costs by turning those predictions into time dependent travel matrices and graph features.
- Search for feasible routes that optimize distance, service levels and operating constraints, then repeat when conditions change.
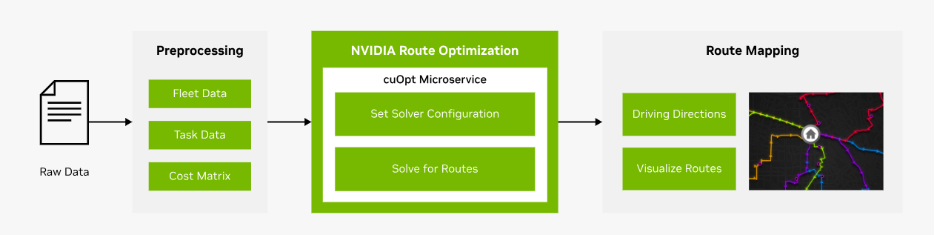
NVIDIA has effectively productized this pattern with cuOpt and the route optimization AI workflow, designed for near real‑time re‑optimization.
How AI-based Route Optimization Training on GPU Works?
Before a solver can search, it needs a view of how the network will behave in the next hour, not just the last hour.
Predictions on GPUs
Spatiotemporal traffic and ETA models are compute heavy during training and must serve many queries per minute at inference.
Keeping forecasts fresh improves the quality of time dependent costs, which reduces late penalties without adding vehicles.
For example, Domino’s has discussed real‑time route planning with sub‑second runtimes built with NVIDIA technology.
Graph and cost building on GPUs
At city scale, batches of shortest paths, k‑nearest stop lookups and clustering become expensive.
With the NetworkX cuGraph backend, teams commonly see up to 50 to 500 times more acceleration on large graphs with zero code changes, which shortens cost rebuilds so you can re‑optimize during the route.
The net effect is simple. Predictions keep costs honest, GPU graph work keeps them fresh and the solver receives inputs that reflect current conditions.
How do GPU Solvers Search the Route Space?
Metaheuristics dominate practical routing. They create an initial solution, then improve it by exploring large neighborhoods of possible moves. GPUs accelerate the expensive inner loop:
- Parallel initial construction builds many promising seeds at once and repairs them to feasibility
- Massively parallel local search evaluates thousands of insertions, swaps and ejections per pass with fast checks for time windows and capacities
- Population based improvement evolves many solutions in parallel, applies large neighborhood moves, then reduces to the best set
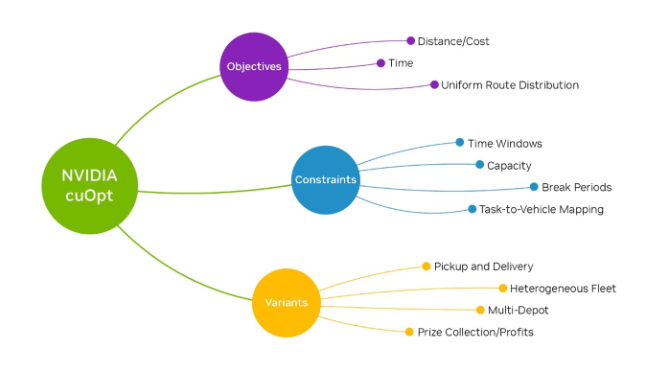
NVIDIA reports that cuOpt analyzes billions of feasible moves per second and has achieved multiple world records on standard routing benchmarks. The emphasis is not only solution quality but time to solution, which makes continuous replanning possible.
Key Results of AI-Based Route Planning on GPU
When GPUs come in the picture, three shifts show up quickly, with numbers you can cite internally:
Replan latency drops
GPU acceleration moves you from minutes to seconds, enabling trigger‑based replans when a freeway clogs, an urgent order lands or a picker slips.
Miles fall at the same service level
UPS’s ORION program, a large‑scale example of continuous route optimization, reported 6 to 8 miles reduced per route and projected $300–$400 million in annual savings at full deployment, plus 10 million gallons of fuel and 100,000 metric tons of CO₂ avoided annually.
Costs tie back to the P&L
Average trucking cost in 2024 was $2.26 per mile, with fuel a major component. Reducing miles touches fuel and time, so routing payback is visible in monthly reports.
AI-Based Route Planning on GPU: Practical Implementation Checklist
Now that you’re well-acquainted with how AI-based route optimization works with GPU acceleration, it’s time to ensure the best practices.
Set Objectives and Baselines
Begin by agreeing on a small set of outcomes you want to move, typically on-time rate, miles per stop and replan latency.
Pull 30 to 60 days of recent routes and telemetry to establish a clean baseline and quantify where you stand today.
Define first-phase targets for a single pilot region, outline a clear change window for go-lives and document rollback rules so operations never stall if something misbehaves.
Prepare and Validate Data
Routing succeeds or fails on data hygiene, so standardize addresses and geocodes and give dispatchers a quick path to correct bad points. Keep time windows and service times in one format with sensible defaults by stop type when fields are missing.
Centralize vehicle capacities, driver skills, shifts and breaks so the solver never guesses. Run a light nightly validation that flags overlaps, outliers and gaps. Quarantine suspect records with a reason code and fix them before the next planning cycle.
Build Predictive Signals
Start with compact models that matter immediately. Predict dwell times and improve ETA accuracy using historical speeds, live traffic, weather, stop type and time of day.
Refresh predictions every few minutes in dense zones and every 10 to 15 minutes elsewhere so costs reflect the world as it is, not as it was.
Track ETA error by zone and time bucket. Once the loop is stable, layer in graph or sequence models for additional lift.
Construct Travel Costs at Speed
Your optimizer needs travel times that match the moment. Maintain a canonical road graph with speed profiles and turn penalties and use GPU batch shortest paths to rebuild origin-destination matrices by zone.
Cache what does not change and invalidate only the tiles where speeds drift beyond a set threshold. Add light clustering so the solver starts from sensible territories rather than reshuffling everything on each solve.
Expose a Reliable Solver API
Treat optimization as a simple, predictable service. Inputs should include stops with geocodes, windows and service times and a fleet description with capacities, skills, shifts and breaks.
Outputs should include a route sequence, ETAs, planned service start, expected distance and time and a clear feasibility flag.
Keep the first objective set focused on distance and lateness with a gentle penalty for early arrivals. Timebox each solve so dispatch knows what to expect and if a request times out, serve the last feasible plan to keep the day moving.
Instrument a Closed-Loop Dispatch
Connect the plan to what happens on the road. Driver apps should record arrival and departure with quick scans and capture simple exception reasons.
Stream positions every 15 to 30 seconds and correct device clocks on the server so timestamps stay consistent.
Trigger replans only when it matters, for example when an unassigned order ages past a threshold, when ETA slippage exceeds a set number of minutes, when queue depth spikes or when speeds drop sharply on a corridor in use.
Log every trigger to tune thresholds after a week in production.
Measure Outcomes and Prove Value
Prove value with numbers the field respects. Watch the on-time rate, miles per stop, late penalties and driver overtime.
On the system side, track solver success rate, p95 replan latency and the share of requests that hit timeouts.
Run one to two weeks in shadow mode where the GPU plan is computed but the legacy plan is dispatched, then A/B a single dense zone by postcode to see real impact with low risk.
Choose Build vs Buy Pragmatically
If your constraints match standard last-mile or field service patterns and you want time to value, buy a GPU-accelerated solver and wire it in.
If your rules are unusual or you need tight coupling with a proprietary TMS, build a thin service that encodes your constraints while still using GPU graph tools for fast cost building.
Guard against lock-in by keeping your schemas open, abstracting the solver behind an internal API and exporting candidate plans in a neutral format.
Secure and Audit the Stack
Protect access with roles for dispatchers, supervisors and auditors. Keep customer details out of routing payloads where practical and store them separately.
Record who triggers replans, changes parameters or approves overrides so you can retrace decisions when needed.
Drill for traffic feed loss, a mapping outage or GPU saturation each quarter and confirm the system degrades gracefully.
Train Teams and Manage Change
Set crews up for success with concise playbooks. Show dispatchers how to approve a replan, handle a missed window or swap a vehicle mid-shift. Keep driver tasks minimal with scan-in, scan-out and a short list of exception reasons.
Hold weekly feedback sessions with operations to surface rough edges and fix the largest source of variance first, whether that is a bad geocode cluster or a dwell model that misses during festivals.
Roll Out in Four Weeks
Use a short, disciplined timeline. Start with goals, a data audit and baseline extraction.
Validate the travel-time matrix and prediction freshness on a GPU node, then deploy the solver in shadow mode and compare feasibility and plan quality.
Move to an A/B in one dense zone using clear replan triggers. After four weeks, review KPIs and either scale to a second zone if targets hold or fix the biggest gap and repeat the cycle.
Control Costs and Plan Capacity
Right-size your GPU pool for peak solves per hour with room to spare. Autoscale on queue depth and the age of the oldest request so you pay for capacity only when needed.
Track GPU minutes per solve and set daily budget alerts, so spend is never a surprise.
Push heavy retraining and full matrix rebuilds to off-peak hours to keep daytime capacity focused on replans.
Avoid Common Pitfalls
Do not let dirty geocodes and unrealistic service times force infeasible plans. Resist the urge to add every objective at once.
Start with distance and lateness and expand once the loop stabilizes. Do not replan so often that drivers feel whiplash.
Cap frequency and demand a reason for manual overrides. Always keep a CPU fallback and the last feasible plan so dispatch can operate through any dependency blip.
Confirm Readiness Before Scale
Scale when the basics are green.
You should have approved targets, a week of clean validation, a prediction service that meets latency and accuracy goals, a cost build that completes inside its time budget for your pilot size and a solver that hits its p95 latency and success targets in staging.
Ensure two pilot teams have tested the app end-to-end and that runbooks and rollback steps have passed a dry run. When those gates are met, expand confidently.
Deploy Route Planning Algorithms with AceCloud!
AI driven routing works best as a continuous loop. You predict speeds and dwell, rebuild costs, then search routes again as reality changes. GPUs let you run that loop fast enough to influence the day, not just plan the morning.
AceCloud provides ready access to modern NVIDIA GPUs, optimized runtimes and a deployment path that works with the tools you already use, including cuOpt and RAPIDS. We recommend you start small in one region, scale capacity during peaks and pay only for what you use.
Our managed support keeps latency, reliability and costs on target, so your teams focus on operations, not infrastructure. If you want to cut planning time and operating costs, move a pilot to AceCloud’s Cloud GPU and benchmark it against your current routes. Most fleets see the payback in weeks, not quarters.













