In 2025, Large Language Models (LLMs) are no longer just a buzzword, they’re the backbone of artificial intelligence (AI) innovation. From powering conversational agents like chatbots to generating creative content, analyzing complex datasets, and even assisting in scientific breakthroughs, LLMs have transformed how we interact with machines. These models, built on vast neural networks, can understand and generate human-like text with unprecedented accuracy, making them indispensable across industries.
But what exactly are LLMs? At their core, their AI systems trained on massive datasets to predict and generate text based on patterns learned during training. By 2025, advancements in hardware, algorithms, and data strategies have pushed LLMs to new heights, enabling them to handle tasks beyond text – like images, audio, and code while becoming more efficient and accessible.
This blog explores the technical underpinnings of LLMs, their evolution and what you need to know to leverage them effectively in 2025.
What are Large Language Models?
Large Language Models are neural networks trained on vast collections of text data to understand, generate, and manipulate human language. Based on the transformer architecture introduced by Vaswani et al. in 2017, these models are capable of learning complex patterns in language across different tasks, including text completion, question answering, translation, and reasoning.
Core Characteristics:
| Feature | Description |
| Model Architecture | Primarily Transformer-based, featuring self-attention mechanisms. |
| Training Objective | Typically uses unsupervised objectives like next-token or masked prediction. |
| Parameter Scale | Ranges from millions to hundreds of billions of parameters. |
| Data Sources | Web pages, books, code repositories, social media, technical manuals, etc. |
The Evolution of LLMs: A 2025 Perspective
The journey of LLMs began with early language models like RNNs (Recurrent Neural Networks) and LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory Networks), which struggled with long-range dependencies in text. The game-changer came in 2017 with the introduction of the Transformer architecture in the paper “Attention is All You Need” by Vaswani et al. This shift from sequential processing to parallelized attention mechanisms laid the foundation for modern LLMs like BERT, GPT, and their successors.
By 2025, LLMs had evolved significantly. Models like GPT-4 (2023) paved the way for multimodal capabilities, but today’s models – think hypothetical successors like GPT-5 or xAI’s Grok 3 integrate text, images, and even real-time data processing. The focus has shifted from sheer size (parameter count) to efficiency, interpretability, and domain-specific tuning. Open-source initiatives and smaller, optimized models have also democratized access, making LLMs viable for startups and individual developers.
Technical Foundations of LLMs
To understand LLMs in 2025, we need to unpack their technical core. Here’s a breakdown:
Transformer Architecture
The Transformer remains on the bedrock of LLMs. It consists of:
- Encoder-Decoder Structure: Early models like T5 used both, but decoder-only models (e.g., GPT) dominated generative tasks in 2025.
- Self-Attention Mechanism: This allows the model to weigh the importance of each word in a sequence relative to others, capturing context efficiently.
- Multi-Head Attention: Multiple attention layers run in parallel, enhancing the model’s ability to focus on different aspects of the input.
- Positional Encoding: Since Transformers don’t process sequentially, positional encodings embed word order information.
Enhancements like sparse attention (reducing computational load) and longer context windows (up to 128K tokens) will be standard in 2025.
Training Paradigms
LLMs are pre-trained on vast corpora – think trillions of tokens from books, web pages, and code repositories – using unsupervised learning. Techniques include:
- Next-Token Prediction: Predict the next word in a sequence (e.g., GPT-style).
- Masked Language Modeling: Predict masked words in a sentence (e.g., BERT-style).
- Fine-Tuning: Post-pre-training, models are tuned on smaller, task-specific datasets.
Parameters and Scale
Parameters are the weights in the neural network, determining a model’s capacity. In 2025, while trillion-parameter models exist, efficiency-focused models (e.g., 10B-50B parameters) with techniques like quantization and pruning are gaining traction.
Table 1: Evolution of LLM Scale
| Model | Year | Parameters | Key Feature |
| GPT-3 | 2020 | 175B | Massive scale |
| BERT | 2018 | 340M | Bidirectional context |
| Grok 3 | 2025 | ~500B (est.) | Real-time reasoning |
| LLaMA | 2024 | 70B | Open-source efficiency |
How LLMs Work: From Data to Deployment
Data Preprocessing and Tokenization
Raw text is messy – LLMs need structured input. In 2025:
- Tokenization: Text is split into tokens (words or subwords) using algorithms like Byte-Pair Encoding (BPE). Modern tokenizers handle multilingual and multimodal data.
- Cleaning: Noise (e.g., typos, HTML tags) is removed, and datasets are deduplicated to improve quality.
Training Process
Training a Large Language Model (LLM) in 2025 is a high-cost, compute-heavy process involving:
- Pre-Training: Models are trained on trillions of tokens (text/code) over weeks using thousands of GPUs or TPUs. Datasets exceed 10T tokens.
- Optimization: Algorithms like AdamW and LAMB are used. Mixed-precision training (FP8/BF16), ZeRO, and parallelism techniques improve speed and efficiency.
- Hardware Landscape:
- NVIDIA Blackwell B100/B200: Industry-leading GPUs with up to 20+ PFLOPS and 192GB HBM3e memory.
- H200: Still in use but being replaced by Blackwell.
- Google TPU v6: Powers Gemini models; used internally at Google.
- AWS Trainium2 / Intel Gaudi3: Gaining traction in cost-efficient, large-scale training.
- Cerebras, Groq: Specialized chips for niche workloads.
Training a top-tier model can take 30–90 days and cost $30M–$100M+. To handle this demand efficiently, many organizations deploy Kubernetes GPU clusters that orchestrate high-performance compute workloads across thousands of GPU-enabled nodes.
Inference and Fine-Tuning
- Inference: Post-training, LLMs generate text by sampling from probability distributions (e.g., top-k sampling).
- Fine-tuning: Models are adapted for specific tasks (e.g., medical diagnosis) using labeled data, often via techniques like LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) to save resources.
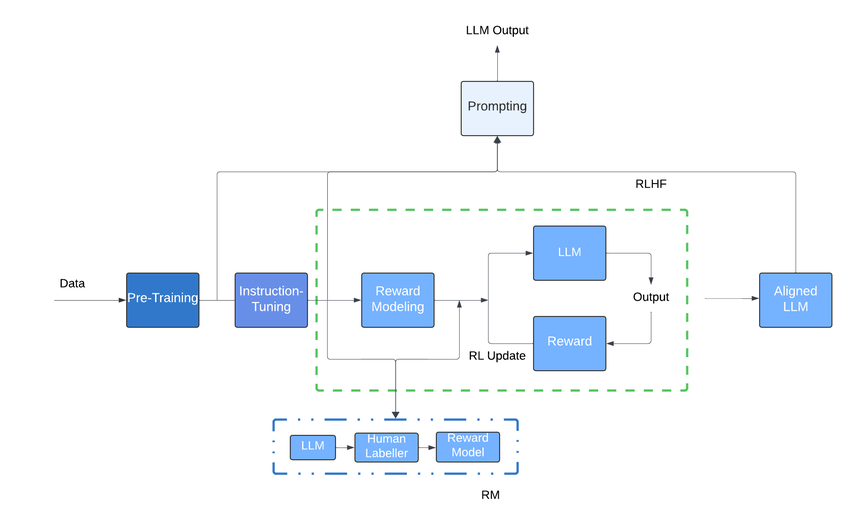
Key Advancements in LLMs by 2025
Multimodality
LLMs in 2025 aren’t text-only. Models like hypothetical “VisionGPT” integrate:
- Text + Images: Generate captions or describe scenes.
- Audio: Transcribe speech or generate voice responses.
- Code: Write and debug software in real-time.
Efficiency and Optimization
- Model Compression: Techniques like quantization (reducing precision from FP32 to INT8) and distillation (shrinking large models) cut costs.
- Sparse Models: Only activate relevant parameters, slashing compute needs.
- Edge Deployment: TensorFlow Lite and ONNX enable LLMs on mobile devices.
Ethical and Sustainable AI
- Bias Mitigation: Tools like fairness-aware training reduce skewed outputs.
- Green AI: Energy-efficient training (e.g., carbon-neutral data centers) addresses the environmental footprint.
Table 2: Efficiency Techniques in 2025
| Technique | Description | Benefit |
| Quantization | Reduces numerical precision | Lower memory use |
| Distillation | Transfers knowledge to a smaller model | Faster inference |
| Sparse Attention | Focuses on key tokens | Reduced compute |
Applications of LLMs in 2025
By 2025, Large Language Models (LLMs) have woven themselves into the fabric of daily life, driving innovation across diverse sectors with their ability to process and generate human-like text. Their versatility stems from advancements in scale, fine-tuning, and multimodal integration, enabling them to tackle complex, real-world challenges. Here’s how they’re making an impact:
- Healthcare: LLMs are revolutionizing medical practice by analyzing vast troves of unstructured data, such as patient records, clinical notes, and research papers. For instance, a doctor might input symptoms into an LLM-powered tool, which cross-references them against millions of medical texts to suggest potential diagnoses – think rare diseases that might otherwise go unnoticed. Beyond diagnostics, these models generate concise research summaries, helping scientists stay abreast of the latest findings without wading through endless journals. In 2025, models fine-tuned on medical corpora even assist in drafting treatment plans, though human oversight remains critical.
- Education: Personalized learning has reached new heights with LLMs acting as adaptive tutors. Imagine a student struggling with calculus: an LLM assesses their weak points via interactive quizzes, then crafts tailored explanations or practice problems in real-time. These systems adapt to individual learning styles – visual learners get diagrams, while verbal learners receive detailed breakdowns. In classrooms, LLMs generate lesson plans or grade essays, freeing educators to focus on mentorship.
- Creative Industries: The line between human and machine creativity blurs as LLMs churn out novels, movie scripts, and marketing campaigns. A screenwriter might collaborate with an LLM to brainstorm plot twists, feeding it a premise and receiving a dozen creative directions in minutes. In advertising, LLMs craft catchy slogans or personalize ad copy based on consumer data, boosting engagement.
- Software Development: Building on tools like GitHub Copilot, 2025 sees LLMs that don’t just suggest code snippets – they architect entire applications. A developer specifies requirements (e.g., “Build a REST API for a blog”), and the LLM generates functional code in Python, JavaScript, or Rust, complete with error handling and documentation. These successors debug code, optimize performance, and even explain their logic, acting as tireless pair programmers.
- Real-Time Analytics: LLMs excel at distilling insights from dynamic data streams like news feeds or social media. In 2025, businesses deploy them to monitor trends – say, tracking sentiment about a product launch on X in real-time. Journalists use LLMs to summarize breaking stories, while financial analysts parse earnings reports for instant market predictions. Enhanced with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), these models pull in fresh data, ensuring outputs stay relevant and accurate.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their power, LLMs face hurdles in 2025:
- Hallucinations: Models invent facts when uncertain – still a work in progress.
- Bias: Training data biases (e.g., cultural skews) persist, though mitigated.
- Compute Costs: Training trillion-parameter models remains expensive, though edge solutions help.
- Interpretability: Black-box nature complicates trust and debugging.
LLMs vs. Other AI Models: A Comparison
How do LLMs stack up against other AI systems in 2025?
Table 3: LLMs vs. Other Models
| Model Type | Strengths | Weaknesses | Use Case |
| LLMs | Language understanding | High compute needs | Text generation |
| CNNs | Image processing | Limited to visuals | Computer vision |
| RNNs | Sequential data | Slow, memory-intensive | Time series |
| Small Models | Efficiency, edge use | Less powerful | IoT devices |
Future Trends for LLMs Beyond 2025
As we peer beyond 2025, the trajectory of Large Language Models promises a leap into uncharted territory. Fueled by breakthroughs in AI research, hardware, and societal needs, LLMs are poised to evolve from powerful tools into transformative forces. Here’s what lies ahead:
- Autonomous Agents: LLMs are on track to become fully autonomous AI agents capable of independent reasoning and decision-making. Picture an LLM managing a supply chain: it analyzes demand forecasts, optimizes shipping routes, and negotiates with vendors – all without human prompts. By integrating planning algorithms (e.g., Monte Carlo Tree Search) and memory systems (e.g., episodic recall), these agents handle multi-step tasks over days or weeks. Beyond 2025, expect them in roles like virtual project managers or personal assistants that anticipate your needs before you ask.
- Quantum Boost: Quantum computing could redefine LLM training, slashing the time and energy required. Today’s models take weeks on GPU clusters; quantum systems, with their ability to solve optimization problems exponentially faster, might train trillion-parameter models in days. Companies like IBM and Google are already prototyping quantum hardware – by 2030, LLMs could leverage quantum annealing to fine-tune weights or samples from vast probability spaces, unlocking new levels of performance.
- Hyper-Personalization: Future LLMs will mold themselves to individual users with uncanny precision. Imagine a model that learns your writing style, humor, and preferences from a few interactions, then crafts emails, stories, or code in your unique voice. Beyond 2025, continual learning lets these models adapt in real-time – say, adjusting to your mood based on tone or context clues. Privacy-preserving techniques like federated learning ensure this personalization happens without compromising data security, making LLMs intimate digital companions.
- Regulation: As LLMs grow more powerful, governments will step in with stricter oversight. Beyond 2025, expect global frameworks tackling bias, misinformation, and energy use. The EU’s AI Act (evolving from 2024) might mandate transparency in LLM training data, while the U.S. could enforce “right to explanation” laws, requiring models to justify outputs. Ethical guidelines will push developers to prioritize fairness and accountability, balancing innovation with societal trust.
Conclusion
In 2025, Large Language Models will be a technical marvel – powerful, versatile, and increasingly accessible. From their Transformer roots to multimodal frontiers, LLMs have redefined AI’s potential. Yet, they’re not without challenges: efficiency, ethics, and interpretability remain focal points for innovation. Whether you’re a developer, researcher, or business leader, understanding LLMs’ technical intricacies equips you to harness their capabilities effectively.
As we stand on the cusp of even greater breakthroughs, one thing is clear: LLMs are not just tools – they’re partners in shaping a smarter, more connected future. Dive in, experiment, and see where these models can take you in 2025 and beyond.












