Introduction
Deep learning, a crucial subset of artificial intelligence (AI), is revolutionizing industries from healthcare to autonomous driving. By mimicking the structure of the human brain, deep learning uses artificial neural networks to process large amounts of unstructured data like images, audio, and text.
However, training these models requires significant computational power, which is where cloud GPUs come into play. Cloud-based Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) offer the speed, scalability, and cost-effectiveness needed to train deep learning models efficiently, enabling businesses to leverage AI capabilities at unprecedented levels.
In this blog, we will explore how deep learning works, different model types, and how cloud GPUs accelerate the process.
What is Deep Learning?
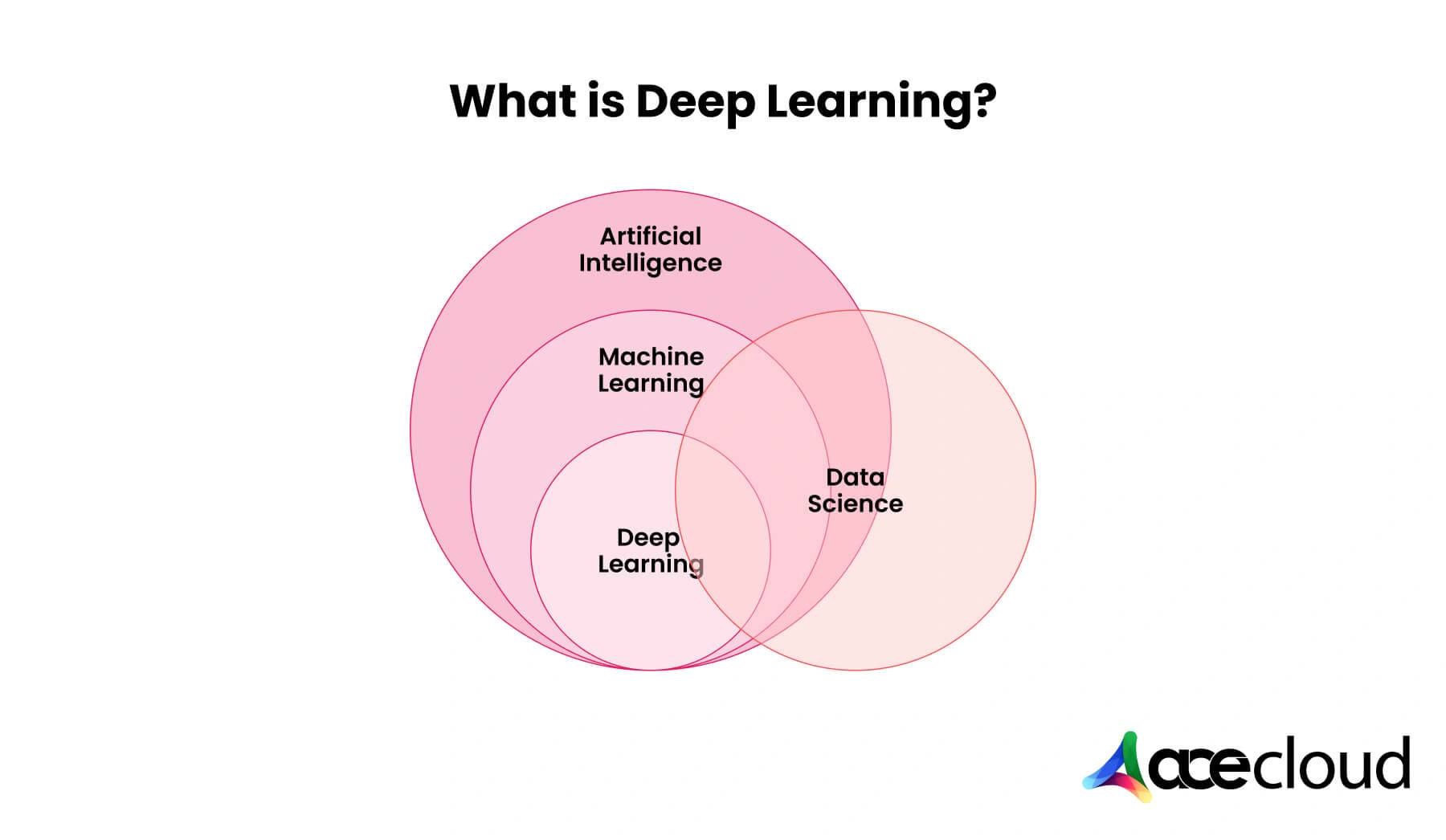
Deep learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that mimics the structure of a human brain to process big data. It sets up the pattern analysis with artificial neural networks, which comprise layers of neurons.
Deep learning has changed the face of various healthcare industries to autonomous driving, maximizing automation, and enhancing decision-making systems.
Although deep models can do wonders, they require enormous computing power due to their complexity and large datasets needed for training.
Cloud GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) solve this problem by offering the necessary power to train these deep learning models efficiently.
How Does Deep Learning Work?
Multiple layers are used to make deep learning models with artificial neural networks. Data is fed through layers, and every layer transforms the data to feature extraction and prediction generation. Here’s how it works in a nutshell:
- Data Input: Generally, unstructured data in the forms of images, videos, text, or audio feed into the model.
- Feature Extraction: The neural network processes the data through multiple layers, which extracts features for the technique.
- Backpropagation: When we let the weights of the network flow using backpropagation, an error-computed model is minimized.
- Prediction: Having done all that, using input data, a model can proceed to make predictions.
Cloud GPUs speed up this process by speeding up parallel computation, which makes the training times for complicated models even quicker.
Types of Deep Learning Models
Many different models in deep learning specialize in serving a particular purpose. Here are a few of the most used models:
1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
CNNs are mainly used in image processing tasks. They use convolution operations to capture spatial hierarchies from data. CNNs are very helpful in image recognition, object detection, and even video processing.
Key Features:
- They reduce the manual process of feature extraction.
- They are excellent at dealing with image data and recognizing the patterns, edges, and texture.
Example: CNNs are very common in facial recognition technology and medical image analysis.
2. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
RNNs are designed to deal with sequential data in a number of applications. Thus, they are particularly useful when the notion of time or order is important in the task. They are widely applied in areas such as NLP, time-series analysis, and speech recognition.
Key Features:
- RNNs learn to remember information from earlier time steps, making them suitable for predicting sequences.
- They suffer from the vanishing gradient problem, and recent sophisticated versions such as LSTM help with this issue.
- Application: RNNs in language models for speech-to-text systems and machine translation.
3. Autoencoders and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
Autoencoders are unsupervised models mainly used for dimensionality reduction and data compression. It consists of an encoder that compresses the data and a decoder reconstructing the original data from the compressed version. VAE is the advanced version, which generates new data similar to input data.
Key Features:
- Useful for feature learning, anomaly detection, and data denoising.
- VAEs benefit in generating synthetic data.
Example: Autoencoders can compress large datasets or generate high-quality synthetic images.
4. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
The GANs consist of two neural networks, the generator and the discriminator, that compete against each other. The generator tries to generate real-looking data, and the discriminator tries to differentiate real from fake data. The kind of competition that these two types of networks face each other results in extremely realistic outputs.
Key Characteristics:
GANs are used in data augmentation, image synthesis, and video generation. They work best in the creative domain, particularly in artwork and video game design.
Example: The diffusion models generate hyper-realistic deepfakes and improve low-resolution images.
5. Diffusion Models
Diffusion models are probabilistic models that generate data through an iterative process that refines noise into structured data. Diffusion models exhibit excellent performance in generating high-quality images and videos, making them a relatively recently developed but highly significant approach to deep learning.
Key Features:
- They involve a reverse diffusion process; a step-by-step noise-to-data transformation.
- They are experiencing popularity in the latest generation of high-resolution images.
Example: Diffusion models produce highly realistic images for use in creative industries.
6. Transformer Models
Transformers are the primary foundational models applied to perform most NLP tasks, including machine translation, text summarization, and question/answer systems. They utilize the self-attention mechanism, making them better suited for working with text data.
Key Features:
- Transformers do not process their data in sequence as RNNs do, which makes their training faster
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder. Representations from Transformers) and GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer) are the two most widely used transformer models.
Example: Transformers are used in the tools Google Translate and in creating content-related systems like OpenAI’s GPT models
Recommended Read: How To Build Your GPU Cluster For AI And Deep Learning
Using Cloud GPUs for Deep Learning
Cloud-based GPUs for deep learning allow for the training and deployment of these models at scales. They are faster, more flexible, and cost-effective than traditional hardware configurations. Here is a summary of some common applications:
1. Image and Video Analysis
Healthcare and entertainment-focused industries rely heavily on CNN for image and video analysis. Cloud-based GPUs make it much faster to process images, making it important for medical imaging diagnostics, video content moderation, and vision systems for autonomous vehicles.
2. NLP (Natural Language Processing)
RNNs and transformers are also crucial for NLP applications, such as sentiment analysis, text generation, and translation. Cloud GPUs accelerate the training of such large models, allowing companies to build real-time chatbots, virtual assistants, and translation services.
3. Data Compression and Anomaly Detection
Autoencoders and VAEs are applied in industries where big data is handled, like finance and telecommunication, for compressing the data and anomaly detection. Cloud GPUs aid in training these models efficiently and at scale.
4. Synthetic Data Generation
GANs are applied to fields requiring synthetic data, such as robotics and gaming. Cloud GPUs enable the fast generation of high-quality synthetic images, videos, and 3D models.
Top Industries Applications:
- Healthcare: Cloud training of deep learning models on GPUs is being used in medical image analysis, drug discovery, and genomics. For instance, CNNs can spot early symptoms from X-rays and MRIs, and GANs can produce synthetic data for medical research purposes.
- Self-driving Cars: Autonomous car companies use deep learning models, such as CNNs and RNNs, to develop images from cameras, radar, and LIDAR systems. Cloud GPUs make it possible to train that model, which would allow cars to drive safely in the real-time environment.
- Finance: In finance, RNNs and autoencoders are applied to analyze time-series data, detect fraud, and manage risk. Financial institutions have now realized speedy analysis of large data volumes through cloud GPUs, improving decision-making and security.
- Entertainment: The GANs and diffusion models applied in the entertainment sector create high-resolution visual effects, game environments, and even deep fakes. Cloud GPUs offer cost-effective training and deployment, allowing for fast-paced content creation.
Conclusion
Cloud GPUs are the heart of deep learning – faster training, more scalable, and cheaper model development. Whether the field is image recognition, NLP, or data generation, cloud GPUs push industries further into what’s achievable with deep learning. As deep learning models continue to grow in complexity, demand for cloud GPUs will only increase as a dominant tool in the future of AI innovation. Book a free consultation with an AceCloud expert today.













