As your data volumes and model complexity grow, classical infrastructure eventually becomes a bottleneck. Therefore, you need an execution model designed for scale. High-Performance Computing (HPC) brings clustered servers, fast interconnects and parallel software together, so you can solve problems that overwhelm single machines.
High-Performance Computing (HPC) uses clusters of CPU/GPU nodes connected by low-latency networks to solve large-scale problems quickly. It’s ideal for simulations, data analytics and AI training where massive compute is required.
- In 2024, total HPC-AI spending reached about $60 billion with 23.5% year-over-year growth, the fastest expansion in two decades.
- TOP500 confirms three exascale systems in production, delivering about 20.61 exaflops of aggregate peak and roughly 137.6 million total cores.
This shows how far parallelism has scaled. Moreover, modern HPC spans on-premises clusters and cloud platforms, which lets you align cost and agility with business goals. Let’s find out more about high performance computing.
What is High-Performance Computing?
HPC is a tightly connected set of servers that behave like a single logical computer. Clusters pair CPU and GPU nodes with a low-latency fabric and a parallel file system, so applications progress without waiting on data or coordination.
In practice, an HPC cluster aggregates compute nodes through a low-latency fabric and exposes them as a single logical resource. Because work is parallelized across nodes, you shorten time to insight for activities like climate modeling, risk simulations or molecular dynamics.
You also gain predictable throughput when pipelines are engineered around the cluster scheduler and file system. The shift to heterogeneous compute is measurable. In 2025, accelerated machines were 46.4% of systems, yet delivered 86.2% of total peak flops, which explains why modern designs prioritize GPUs.
How Does High-Performance Computing Works?
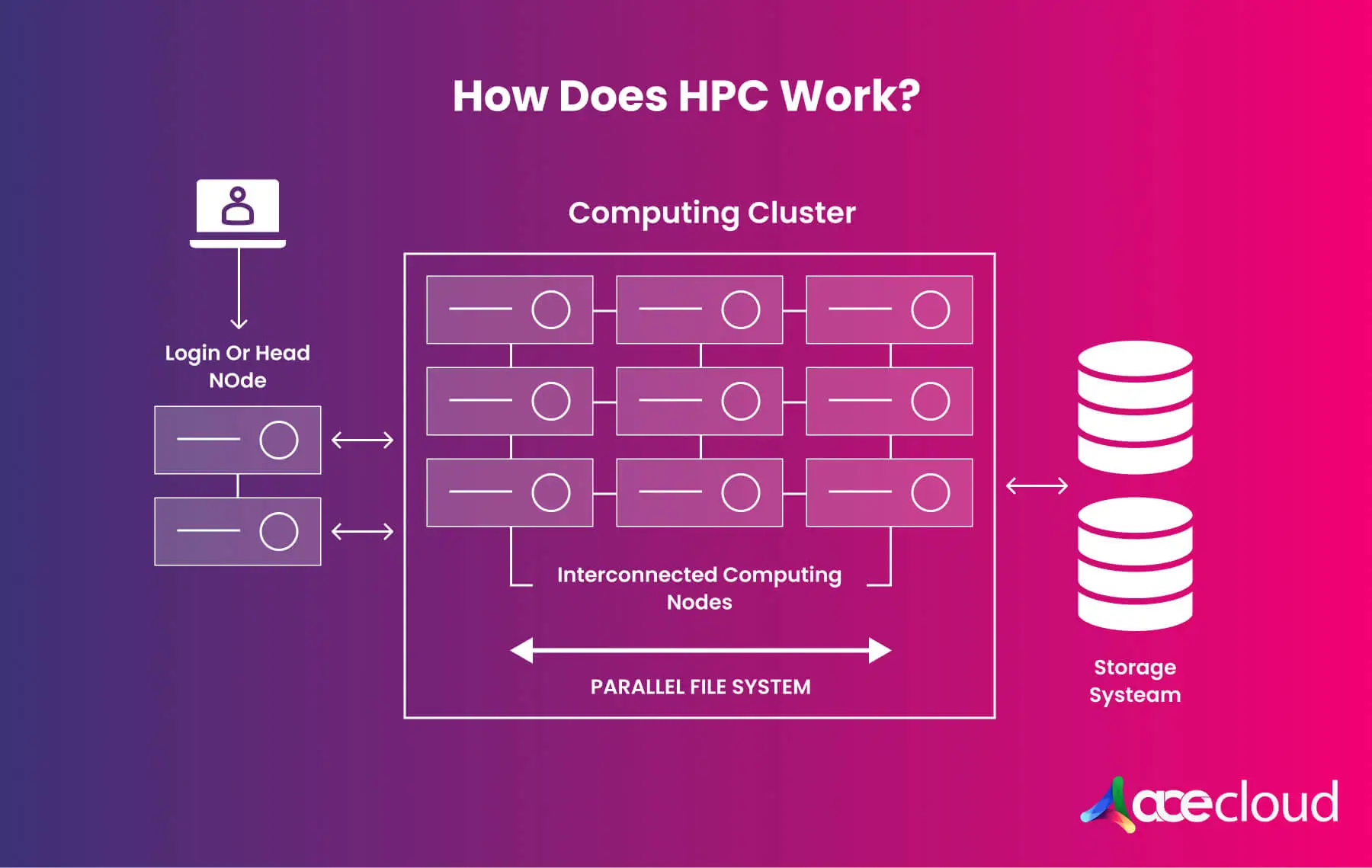
HPC works by breaking large problems into smaller parts, scheduling them across nodes, then moving data quickly enough to keep processors busy.
Parallel models
Most distributed applications use the Message Passing Interface (MPI) for process-to-process communication, with OpenMP for shared-memory threading and CUDA for GPU acceleration. MPI is the de facto portable standard across C, C++ and Fortran, which is why it underpins the majority of large-scale scientific and engineering codes.
Workload scheduling
A scheduler allocates nodes, enforces policy and launches jobs, so multiple groups share the cluster fairly. Slurm is widely used at enterprise scale and reports approximately 65% adoption across TOP500 systems, which signals operational maturity for enterprise programs.
Storage for parallel I/O
Parallel file systems prevent accelerators from idling while they wait for data. Managed Lustre services claim up to terabytes per second of throughput, millions of IOPS and sub-millisecond operations, which are useful targets even when you deploy on premises. Newer capabilities, such as GPUDirect Storage support in Spectrum Scale, reduce CPU overhead and latency by moving data directly between storage and GPU memory.
Networking for low latency
Fabric design governs tightly coupled codes and collective operations. NVIDIA Quantum-2 switches provide 400 Gb/s per port with 64 ports in 1U, which reduces message overhead and improves scaling efficiency across racks.
Direct paths to GPUs
GPUDirect Storage enables a DMA path between NVMe or NVMe-oF and GPU memory, which removes CPU bounce buffers and lowers latency. Multiple vendor briefs and NVIDIA’s guide describe higher sustained bandwidth and lower CPU utilization when GDS is configured correctly.
Note: Without fast interconnects, processors wait on data, wasting cycles. Technologies like InfiniBand and GPUDirect Storage ensure efficient use of GPUs and minimize delays.
HPC vs Quantum Computing
As roadmaps often mix key terms, let’s contrast classical HPC and quantum systems, so you can set realistic expectations.
Architecture
HPC scales classical CPUs and GPUs with parallelism to solve large linear algebra and simulation problems efficiently. Quantum computers use qubits that leverage superposition and entanglement, which allows certain classes of problems to be explored more efficiently than classical bits.
Problem fit
Today’s HPC excels at numerical simulation, graph analytics and data-parallel AI where mature toolchains exist. Quantum systems remain promising for factoring, certain optimization and simulating quantum effects, yet they still face error rates, scale and stability challenges that limit broad enterprise use.
Maturity
The exascale era demonstrates how far classical HPC has advanced, with systems like El Capitan, Frontier and Aurora surpassing exaFLOPS on LINPACK and leading complementary HPCG metrics. Meanwhile, quantum research continues to break records, but enterprises should treat it as exploratory for most production roadmaps.
HPC and Cloud Computing
Since demand is bursty and projects vary, many teams combine on-premises clusters with cloud HPC. Cloud providers expose GPU- and CPU-optimized instances, RDMA fabrics and managed file systems. This helps you to scale out quickly, then scale back to control spend.
As a result, you avoid large up-front capital expense while keeping performance options open through hybrid designs.
A typical cloud pattern uses autoscaling job queues, container images for reproducibility and parallel file services sized for the peak I/O window. For sensitive data, you keep steady workloads on-premises and burst to cloud for short spikes or specialized accelerators.
This approach minimizes queue times without overbuilding your data center. Hyperion’s 2025 market update reported 23.4% growth in on-premises servers and 21.3% growth in cloud use during 2024, which validates hybrid strategies over single-venue bets.
What are the Key Benefits of Cloud-Based HPC?
Let’s quantify benefits for your program across elastic scale, faster provisioning, optimized data paths, security alignment and global collaboration with distributed teams.
Elastic scale for spiky demand
You right-size clusters per project and reduce idle capital between milestones. For interruption-tolerant stages, EC2 Spot instances are priced up to 90% below On-Demand.
Google Spot and preemptible VMs offer 60% to 91% discounts depending on the machine type. Proper checkpointing and flexible instance choices help you capture those savings.
Faster provisioning and iteration.
Reference architectures move teams from request to first job in hours instead of weeks, which increases experiment cadence and reduces time to validated results. Managed schedulers, images and telemetry reduce toil tied to firmware, provisioning and patch orchestration. Thus, you redirect engineering cycles from infrastructure to model development and validation.
Optimized data paths to accelerators
FSx for Lustre advertises multi-TB/s throughput, millions of IOPS and low latency, which helps keep GPUs saturated as datasets grow. Performance documentation ties effective throughput to file system capacity, layout and workload characteristics.
Security alignment without reinvention
Major cloud providers map identity, encryption and segmentation to recognized frameworks, so you codify controls as policy and infrastructure rather than building everything from scratch. For regulated work, align with NIST SP 800-53 and SP 800-171.
Work flexibility
In a global business scenario where multiple teams work on the same project from diverse time zones, employees need to access apps and data remotely. With cloud-based HPC, employees can access their tasks from anywhere, enabling collaboration across teams, departments and geographies.
Practical HPC Architecture Checklist for Enterprises
Now that you understand the fundamentals of High-Performance Computing, let’s discuss a repeatable flow that connects design choices to measurable outcomes.
Profile workloads first
Capture ranks, GPU duty cycle, memory footprints and I/O patterns. Tag jobs as tightly coupled or throughput oriented because that choice drives node sizing, storage tiers and fabric selection.
Choose an orchestrator on purpose
Keep Slurm for batch reservations, fair share and predictable backfill. Introduce Kubernetes where services, micro-jobs or elastic inference help adjacent teams that prefer APIs. Slurm’s large installed base at leadership centers supports this split.
Design storage around concurrency
Target Lustre-class parallel I/O that sustains TB/s-scale throughput and millions of IOPS. Validate stripe policies and caching, so hot data sits near accelerators during runs.
Select the right fabric
Use NDR-class InfiniBand for latency-sensitive collectives and all-to-all exchanges. Confirm performance with microbenchmarks before production cutover, then record switch and host settings as code.
Enable direct GPU data paths
Implement GPUDirect Storage where pipelines move data straight into device memory. NVIDIA documents that GDS removes CPU bounce buffers and reduces latency, which raises GPU duty cycle when configured correctly.
Automate images and environments
Capture compilers, MPI stacks and drivers as versioned artifacts. Roll them out through CI, so clusters reproduce across regions and rollback stays simple.
Establish cost guardrails
Bind queue policies to budgets and quotas. For tolerant stages, route to Spot or preemptible capacity where discounts reach 60% to 91% depending on provider. Track cost per result besides utilization and wait time.
Deploying Kubernetes for HPC
Kubernetes fits workflows that behave like services or many short jobs. NVIDIA’s GPU Operator and Network Operator enable drivers, device plugins and GPUDirect RDMA on supported systems.
GKE documents steps to maximize GPU network bandwidth using GPUDirect capabilities and exposes GPUDirect RDMA on selected machine types. Nevertheless, you should validate pod placement, NUMA alignment and collectives early to confirm latency targets.
Common HPC Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
When using HPC, you will have to apply short checks and design habits that prevent surprises during procurement, deployment and scale-up. You should avoid these pitfalls at all costs.
Under-instrumented pilots
Small datasets seem fine, then parallel I/O collapses at scale. Always test with production sizes before financial commitments, including multi-TB/s storage targets if your workloads demand them.
Fabric treated as an afterthought
A generic network looks inexpensive until collectives dominate your wall clock. Validate communication patterns on the target fabric and confirm 400 Gb/s per-port capabilities when your solvers need it.
One scheduler everywhere
Forcing Kubernetes on tightly coupled solvers or Slurm on micro-services adds friction. Use each where it fits to reduce contention and improve throughput.
Ignoring direct GPU data paths
Skipping GPUDirect Storage leaves accelerators idle while CPUs shuttle bytes. Enable the feature and confirm gains using the vendor’s guidance and tools.
No cost guardrails
Unbounded queues surprise budgets during final sprints. Favor Spot or preemptible where appropriate and bind spending to quotas and dashboards, so leaders see burn rate early.
High Performance Computing Use Cases
HPC has become a critical enabler for many industries, unlocking new capabilities and driving innovation. Below are prominent use cases across sectors.
Healthcare and drug discovery
HPC is transforming healthcare (particularly genomic sequencing) which ingests raw reads, aligns them to reference genomes and identifies variants across billions of bases.
GPU-accelerated pipelines speed alignment, base-calling and deep-learning–based variant calling, while parallel filesystems and fast interconnects keep data moving.
Hospitals and biotechs run population-scale analyses for pharmacogenomics, rare disease discovery and outbreak tracing.
Together, compute and I/O turn weeks of processing into hours, enabling real-time insights and equitable, personalized medicine.
Engineering and manufacturing
Engineering teams rely on HPC for computational fluid dynamics, using GPUs to solve Navier–Stokes systems and accelerate turbulence models and combustion chemistry.
High-I/O meshes and checkpoint files stream over parallel filesystems, enabling faster iterations and runs. Aerospace teams optimize lift, drag and aeroacoustics while automotive engineers evaluate aerodynamics, cooling and in-cylinder combustion.
Coupled with optimization and digital twins, GPU-accelerated CFD shortens design cycles, reduces prototypes and delivers safer, quieter, efficient products.
Entertainment and media
Studios leverage HPC for 3D animation rendering, where GPU-accelerated ray tracing, path tracing and denoising compute billions of light interactions per frame.
Shot data, textures, caches and geometry stream from parallel storage, while schedulers pack jobs across render farms for throughput. Artists iterate interactively with GPU renderers, then scale to final frames at cinematic quality.
The result is faster dailies, fewer artifacts and delivery across commercials, episodic series and feature films.
Oil and gas
The oil and gas sector depends on HPC-driven seismic imaging to transform field recordings into high-resolution subsurface models.
GPUs accelerate reverse time migration and full-waveform inversion, crunching 3D volumes with tight memory and interconnect demands.
High-I/O ingest, staging and checkpointing keep nodes fed while iterations refine velocity models and reduce uncertainty.
Better images de-risk exploration, guide drilling and improve reservoir understanding, reducing costs and environmental impact through more accurate decisions.
Taking the Next Step with AceCloud
Begin with a focused pilot that validates scaling efficiency, I/O behavior and cost per result against one priority workload. We will stand up a Slurm-based GPU cluster with parallel storage and an NDR-class fabric, then benchmark your kernels while mapping controls to your security framework.
Once results meet targets, we will codify the design as code, so teams can scale confidently across projects. At that point, you will have a durable foundation that balances performance, governance and spending.
We designed our platform for teams that need powerful GPUs quickly with predictable networking and a clear SLA. You can launch NVIDIA H100, A100 and L40S, attach managed Kubernetes, then run inside a dedicated VPC. Book your free consultation today and we’ll help you focus on ideal models and best results!
Frequently Asked Questions:
HPC is ideal for tightly coupled simulations, large-scale analytics and GPU-accelerated AI where speed and scale drive business outcomes. These workloads decompose into many tasks that run concurrently across nodes. Consequently, you see meaningful gains when parallel efficiency, low latency and high I/O throughput align.
No. You add GPUs where kernels are compute dense or highly parallel, such as molecular dynamics or model training. CPU-only nodes remain effective for pre- and post-processing, orchestration and tasks that are memory bound rather than compute bound.
Use Slurm for batch scheduling when you need reservations, fair share and predictable queue behavior for MPI jobs. Use Kubernetes for services, short jobs and inference where APIs and autoscaling improve developer flow. In practice, many programs run both to match tools to workload traits.
Measure cost per result rather than cost per node to align with business value. Start with a small benchmark that mirrors production data, then model changes in fabric speed, storage layout and GPU mix. Finally, enforce budgets with queue policies, use interruption-tolerant capacity where safe and track utilization alongside spend.
Treat frameworks like NIST SP 800-53 and SP 800-171 as design inputs, not paperwork at the end. Segment networks, encrypt data in transit and at rest and bind scheduler identities to least privilege roles. Additionally, express policies as code, so posture stays consistent when clusters scale.
Provision a parallel file system that sustains required throughput with correct stripe policies and caching near accelerators. Choose low latency fabrics for MPI collectives and validate with communication microbenchmarks before production. Where data paths touch GPUs, enable GPUDirect Storage and verify topology to avoid CPU mediation.













