DeepSeek AI has surprised the tech industry. On January 27th, just seven days after its release, the DeepSeek AI assistant powered by DeepSeek-V3 surged to the top of the App Store’s free applications, surpassing ChatGPT.
The model’s popularity sent shockwaves in the U.S. tech market, with the NVIDIA chip maker losing close to 589 billion dollars in share value.
But what exactly is DeepSeek? How does it work, and why has it received world acclaim following its release? In this piece, we get into details about DeepSeek and why it gained massive traction among tech enthusiasts and business users alike.
What is DeepSeek?
DeepSeek is a Chinese AI development firm based in Hangzhou. Liang Wenfeng founded the company in May 2023, but it only gained traction on the global stage in January 2025.
DeepSeek focuses on developing large language models (LLMs). In November 2023, the company released its first model to rival ChatGPT and Claude, but it performed poorly compared to its latest DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1 models.
On January 20th, 2025, DeepSeek launched its latest LLMs — DeepSeek-R1 and DeepSeek-V3. The AI assistant DeepSeek-V3 is just as good — if not better — than industry-leading U.S. models such as ChatGPT and is built at a fraction of the cost. It guarantees both efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
DeepSeek-V3 is a general-purpose model, while DeepSeek-R1 is advanced and designed for tasks requiring deeper thinking.
DeepSeek Underlying Architecture
Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture
This is a major aspect that gives it an edge. MoE is an architecture that allows the model to use a specific part of its parameters to accomplish a task. It facilitates efficiency and accuracy.
MoE is the sole design that has made DeepSeek cost-effective for developers. For instance, the latest DeepSeek V3 uses 37 billion active parameters out of the 671 billion available parameters. This decreases computing power, as only a small portion of the model’s parameters can be used simultaneously.
Moreover, the AI self-improves through trial-and-error learning processes, mimicking human learning. This factor contributes to the massive user appeal and strengthens DeepSeek’s superior performance claim.
Key Features of DeepSeek
1. DeepSeek is Open Source
Unlike its counterparts, Deep-Seek is open-source. Developers around the globe have the opportunity to make contributions to its development. This encourages collaboration and creativity in the community.
Programmers can review the code and get a glimpse of how it works. As an open-source model, it democratizes the use of AI capabilities, as developers can leverage its capabilities to build complex applications at lower costs.
With the democratization of AI capabilities, more people who would otherwise be priced out of most proprietary AI models can now build them using AI tools without unbearable costs.
2. Affordable and Efficient
DeepSeek has a significant competitive edge over its general counterparts like ChatGPT.
DeepSeek’s technical report revealed that training the model costs the company approximately $5.576M. This figure is in stark contrast to the billions of dollars invested in the development of popular U.S.-based LLMs like ChatGPT.
It is cost-effective compared to OpenAI’s ChatGPT-4. DeepSeek’s API pricing per million tokens is cheaper than that of OpenAI. For example, its reasoning model, the DeepSeek-R1, costs about $0.14 for a million input tokens, compared to OpenAI’s $2.50 per million input tokens. This is a steal for programmers who seek to build applications using LLM’s capabilities.
3. Large Context Window
Context window constitutes the tokens required to send input and response. DeepSeek excels in supporting a large context window of about 128k tokens. With this, the model can process extensive information for tasks such as:
- Coding: A long context window helps to maintain coherence, especially with a large code repository.
- Data Analysis: Large context windows enable the model to accommodate longer request input, such as huge data sets, analyze the text, and give detailed reports based on data.
Training DeepSeek
So, how did DeepSeek build such a powerful model at a fraction of the cost? It all boils down to training; DeepSeek employed a different approach to training.
In a comprehensive technical report, DeepSeek reveals its approach to training the model, which resulted in low computational power while achieving at-par performance with its peers.
DeepSeek’s training involved new measures, including:
1. Advanced Reinforcement Learning
Let’s return to traditional reinforcement learning (RL), where the model learns to make decisions through interaction with an environment (a real-world scenario). The AI model then receives feedback signals and strives to learn from them over time. However, the downside of traditional RL is the demand for enormous computational power and swathes of data to achieve good performance. In the end, it becomes impractical for firms with limited resources.
DeepSeek introduced model-based reinforcement learning (RL) to combat the limitations of traditional RL. Instead of focusing solely on trial-and-error interactions, it employed a learned model of the environment for simulation, significantly reducing the need for large amounts of data.
2. Meta-Learning
DeepSeek’s meta-learning enables the model to learn when presented with a new scenario without much additional data. The model uses the knowledge it learned before, mimicking human learning. Reduces the need for additional data and reduces the cost.
3. Human-in-the-loop
Human expertise is integrated into the training process through demonstration and feedback to reinforce the model’s learning.
4. Distillation
In LLMS, distillation entails transferring knowledge from a large, complex LLM (teacher) to a smaller, more efficient model (student).
Often, it involves the input element and output. In the case of DeepSeek, this includes:
5. Input
- Teacher model: A larger and more complex model (DeepSeek-R1) trained and fine-tuned.
- Student model: A smaller and more efficient model replicating teacher model performance.
- Training data: Includes data such as task-specific data.
6. Output
The distilled model is more efficient and replicates the performance of the large complex model (teacher model).
The consequence is a smaller and more efficient model that requires less computational power to deliver desired results. This makes the model more suitable for the real world, where organizations struggle with limited budget.
DeepSeek vs. ChatGPT
1. Multimodality
While DeepSeek excels in delivering accurate responses, it lacks ChatGPT’s advanced features, such as multimodal capability. With multimodality, ChatGPT accepts both image and text inputs and generates text outputs. GPT-4 can process different input modalities, perform tasks like image analysis, and generate AI images based on prompts.
However, DeepSeek falls short of this feature and can only accept text inputs.
2. Performance
With regard to performance, DeepSeek-RI and V3 are at par, particularly in answering questions and performing coding tasks. Both models give accurate answers and provide the feature of searching the web for current details.
Look at this data from Artificial analysis and how they compare with ChatGPT on different benchmarks: 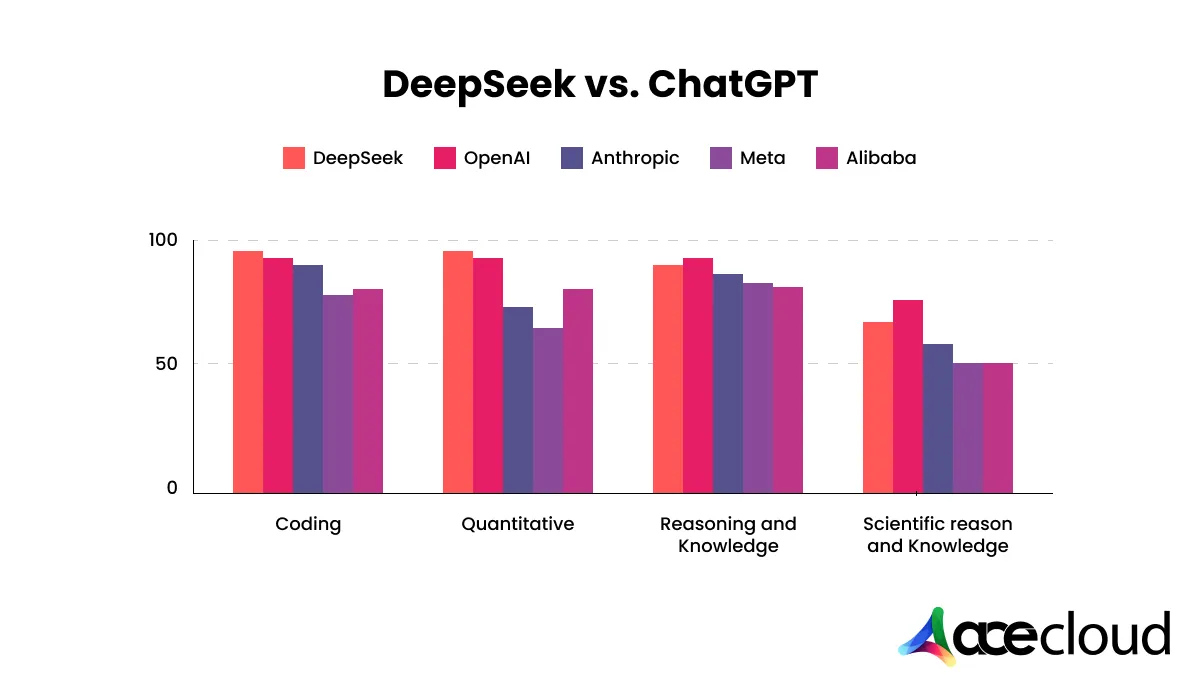
3. Cost
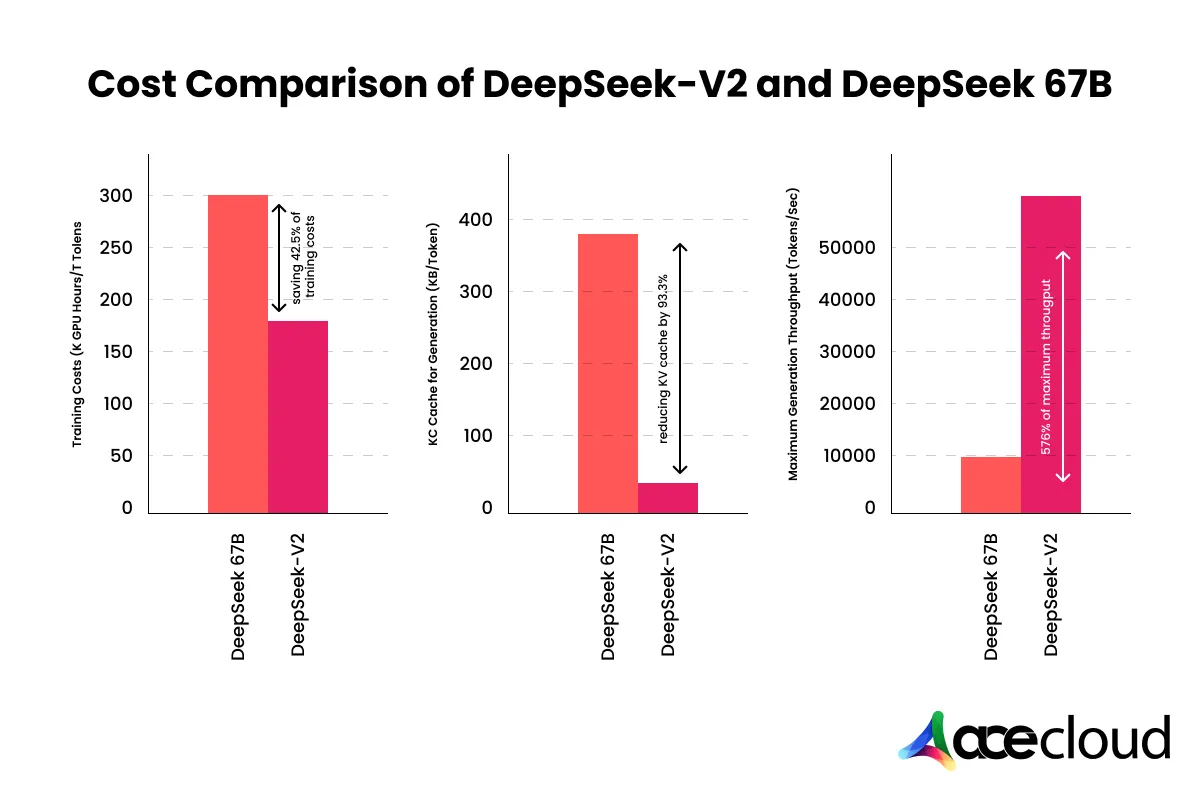
As discussed earlier, the AI assistant (DeepSeek-V3) is free and can be downloaded as an app or accessed through the web version. It starkly contrasts GPT-4, where a user must subscribe for a fee to access the model. Moreover, the DeepSeek API is a cheaper and more affordable option for programmers than ChatGPT.
DeepSeek Use Cases
1. Content creation and summarization
DeepSeek-R1 can generate quality written content from scratch, edit it, and summarize it. Summarizing capabilities allow individuals to gain valuable insights from legal, finance, and other technical report documents.
2. Coding Task
DeepSeek-R1 helps developers write and debug code. It also breaks down and explains complex code, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
3. Data Analysis
DeepSeek contributes to data democratization. Business users without the technical expertise to write queries can interact with data and get actionable insights.
4. Education
Learning is accessible thanks to DepSeek-R1. For example, the model’s mathematical capabilities could be utilized for learning and researching mathematics.
The DeepSeek-R1 model can take huge data sets as input, analyze them based on prompts, and share reports. This allows business users interested in data to gain actionable insights and make rational decisions.
Limitations
- Bias: Like any other model, DeepSeek struggles to make accurate judgments despite being open-source.
- Mixed Languages: The model tends to mix languages, especially when the input is not provided in English or Chinese.
Conclusion
DeepSeek’s capabilities surprised the AI world. It is a groundbreaking technology demonstrating that it is possible to develop AI models with massive capabilities at a low cost. The model is a testament to the possibility of developing efficient and complex LLMs at a lower cost. As it stands, DeepSeek will remain a major challenger to popular LLM models because it provides the same capabilities at a fraction of the cost of other models. Book a free consultation with AceCloud experts to know more about our DeepSeek services.













