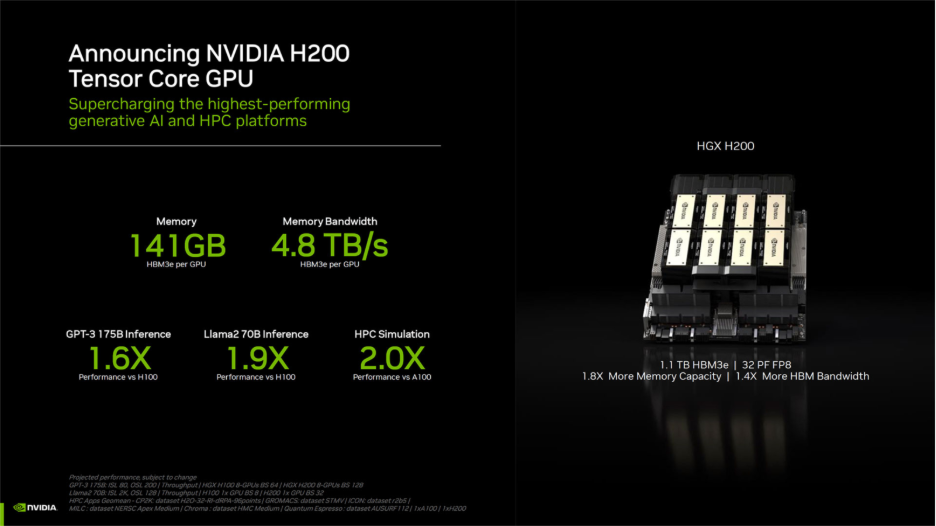
NVIDIA H200 is ideal for AI workloads as it brings 141 GB of HBM3e at up to 4.8 TB per second, lifting capacity and bandwidth together. In practice, its improved capacity boosts several workloads where memory dominates runtime and utilization across pipelines.
For example, it powers AI workloads like long-context LLM inference, retrieval augmented generation with vector search, recommendations and embeddings and graph neural networks.
Together, HBM3e capacity plus high bandwidth lets you keep caches resident, grow batches and remove cross-node complexity. Let’s find out more!
Why AI Workloads Need GPUs?
You can accelerate AI on GPU because thousands of GPU cores run linear algebra in parallel while Tensor Cores target matrix math directly.
Modern inference and training often stall on memory bandwidth rather than raw FLOPs, which puts HBM front and center.
(Source: NVIDIA)
Moreover, GPU systems scale with fast interconnects that preserve utilization across devices. NVIDIA highlights these foundations and notes model execution is frequently memory-bandwidth bound, especially in transformer inference.
Which NVIDIA H200 Features Matter for AI Workloads?
Here we have formulated the NVIDIA H200 specifications to help you quantify its improved performance and capabilities.
| Feature | H200 SXM | H200 NVL |
|---|---|---|
| FP64 | 34 TFLOPS | 30 TFLOPS |
| FP64 Tensor Core | 67 TFLOPS | 60 TFLOPS |
| FP32 | 67 TFLOPS | 60 TFLOPS |
| TF32 Tensor Core* | 989 TFLOPS | 835 TFLOPS |
| BFLOAT16 Tensor Core* | 1,979 TFLOPS | 1,671 TFLOPS |
| FP16 Tensor Core* | 1,979 TFLOPS | 1,671 TFLOPS |
| FP8 Tensor Core* | 3,958 TFLOPS | 3,341 TFLOPS |
| INT8 Tensor Core* | 3,958 TFLOPS | 3,341 TFLOPS |
| GPU Memory | 141GB | 141GB |
| GPU Memory Bandwidth | Up to 4.8 TB/s | Up to 4.8 TB/s |
| Max Thermal Design Power (TDP) | Up to 700W | Up to 600W |
| Form Factor | SXM5 | PCIe, dual-slot (air-cooled) |
| Interconnect | NVIDIA NVLink: up to 900 GB/s; PCIe Gen5: up to 128 GB/s | 2- or 4-way NVIDIA NVLink bridge: up to 900 GB/s; PCIe Gen5: up to 128 GB/s |
To sum up the table:
- 141 GB of HBM3e lets larger models, longer contexts and bigger batches fit on one device. You reduce tensor-parallel fragmentation and host offloads.
- Up to 4.8 TB/s of memory bandwidth reduces stalls in attention, embedding lookups and U-Net passes that are often bandwidth bound. You cut kernel idle time and improve SM occupancy.
- NVLink 4 provides about up to 900 GB/s per GPU, which improves tensor or pipeline parallel scaling and cross-GPU KV-cache or parameter exchange.
- MIG can carve a GPU into as many as seven isolated instances for predictable multi-tenant inference or mixed workloads.
- In NVL configurations, H200 shows roughly 1.4x bandwidth versus H100 with up to 3x larger pooled memory, which helps context-parallel or sharded parameter runs.
7 AI Workloads to Run on NVIDIA H200
We highly recommend reaching for NVIDIA H200 when memory capacity and bandwidth dominate your AI workload. Here we have outlined seven concrete workloads while providing sizing and tuning tips:
1. Long-context LLM inference at scale
AI/ML teams gain throughput because long contexts inflate KV caches and push attention into a bandwidth wall. As you know, larger HBM and faster HBM3e raise batchable tokens before offloads trigger.
According to recent independent benchmarks, you can gain 2.5x higher throughput on H200 when compared to H100 for long-context runs, with additional gains on large model families. That said, prefill remains bandwidth sensitive, which rewards the H200’s wider memory path.
Pro Tip: Favor TensorRT-LLM engines sized to expected sequence ranges, reuse KV caches aggressively and pin model weights to GPU memory to avoid PCIe stalls.
2. Retrieval-augmented generation with vector search
You can accelerate RAG pipelines when the embedding index lives on GPU and rerankers batch efficiently. cuVS reports order-of-magnitude speedups over CPU for indexing and query paths, while Milvus with RAPIDS shows 37x to 91x improvements in common vector search pipelines.
These gains pair naturally with H200’s higher bandwidth and capacity, which allow larger IVF-PQ or graph indexes to stay resident. We suggest you build indexes on GPU with cuVS, size IVF lists to fit in HBM and batch reranking to keep the SMs saturated.
3. Large-scale recommendations and embeddings
Did you know you can reduce step time by keeping larger embedding shards on device and by cutting cross-node communication? NVIDIA reports that embedding communication can reach about 51% of iteration time at scale without specific optimizations.
This confirms bandwidth pressure and motivates bigger on-GPU tables. Techniques like EMBark’s flexible 3D sharding and compression reduce that overhead further. The H200’s additional memory and bandwidth alleviate hot-path lookups and shrink all-to-all pressure.
Pro Tip: Place hot embeddings on HBM, prefer reduction-based clusters for multi-hot features and push internode traffic onto NVLink-connected groups before scaling out.
4. Graph neural networks and graph analytics
NVIDIA H200 helps unlock larger frontier sets and faster samplers because graph workloads are frequently memory bound and irregular. For instance, NVIDIA shows cuGraph-DGL data loading running 2x to 3x faster than native DGL on ~1B-edge datasets with strong multi-GPU scaling.
NetworkX accelerated through cuGraph reports speedups into the hundreds-x on large graphs, which benefits when higher bandwidth keeps kernels fed. H200’s capacity lets you stage bigger features and subgraphs per step.
We suggest you use GPU graph sampling, co-locate feature tensors with partitions and increase sampler fanout only after profiling memory stalls.
5. Genomics pipelines in clinical and research settings
You can shorten turnaround for 30x whole-genome sequencing when alignment, sorting and variant calling stay on GPU. Parabricks documentation cites whole genomes in tens of minutes on GPUs versus roughly 30 hours on CPUs.
This indicates strong sensitivity to memory bandwidth and end-to-end device residency. In our experience, NVIDIA H200’s bandwidth and capacity reduce staging and keep pipeline kernels saturated.
To achieve better performance, keep FASTQ to BAM conversion on device, pin intermediate buffers in HBM when feasible and batch samples to hide I/O latency.
6. Computational fluid dynamics and scientific simulation
NVIDIA H200 is an excellent choice if you need to fit larger meshes and higher-order models while advancing timesteps faster. The GPU manufacturer highlights that H200’s 141 GB HBM3e and up to 4.8 TB/s deliver higher fidelity CFD on fewer GPUs compared with the prior generation.
This directly reflects bandwidth-bound sparse stencils and solver sweeps. More on-GPU state reduces halo exchanges and improves multi-GPU efficiency. We suggest you partition the domains to keep surface-to-volume ratios low, exploit NVLink for halo exchange and raise mesh density only after confirming memory headroom.
7. Diffusion and generative vision models
Step latency improves significantly because U-Net blocks and attention passes often approach memory limits, while TensorRT quantization further amplifies gains.
NVIDIA shows nearly 2x speedups for Stable Diffusion with 8-bit and FP8 paths and newer guides push to 2.4x on recent GPUs.
Higher HBM bandwidth on H200 helps sustain these kernels, especially at higher resolutions where activation maps balloon.
Pro Tip: Use TensorRT or Torch-TensorRT engines, enable attention optimizations and right-size latent and step counts based on profiler HBM metrics.
Explore NVIDIA H200 with AceCloud
H200 shifts the bottleneck conversation from compute to memory capacity, bandwidth and interconnect, which decisively accelerates bandwidth bound AI. You cut nodes, simplify parallelism plans and keep more state residents, which shortens iteration loops and stabilizes throughput under production pressure.
Adopt pragmatically by prototyping on cost efficient fleets today, then targeting H200 where profiles prove memory or bandwidth limits.
AceCloud supports on demand or spot NVIDIA H200 GPUs and managed Kubernetes with multi zone networking and a 99.99%* SLA. Moreover, free migration assistance reduces friction as we move workloads or data to newer GPU generations across environments, including H200 when available.
Frequently Asked Questions:
No, it shines when workloads are memory or bandwidth bound, including long-context LLMs and embeddings. Compute-bound kernels see smaller gains.
NVIDIA H200 is still Hopper. Thus, most gains arrive without code changes, while NVLink topology and MIG configuration remain familiar.
You can run up to seven per GPU, which supports predictable multi-tenant throughput and isolation.
OpenAI received the first DGX H200 and applies it to advanced model training and inference. ThinkDeep uses H100 and H200 in its agentic AI platform for France’s ministries. Additionally, Siemens highlights H200 for faster, higher-fidelity CFD within industrial AI workflows.
Pricing varies by cloud and region, yet Oracle Cloud India lists ₹881.50 per GPU hour, CoreWeave posts ~$50.44 for an 8× H200 node and Azure calculators show $101.76 hourly. However, AceCloud and other India-based GPU providers can save up to 60 percent of your cloud GPU costs!
H200s power the same enterprise AI pipelines where memory becomes the limit, including generative AI in healthcare, finance, manufacturing, media, robotics and public sector. Additionally, adjacent stacks such as data science, simulation and visualization benefit by keeping larger contexts, batches and datasets resident, improving utilization and overall throughput measurably.













